Breast Reconstruction
-
 Mr Andrew Pieri
Mr Andrew Pieri - Updated April 11, 2025
- Created June 9, 2022
What is Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
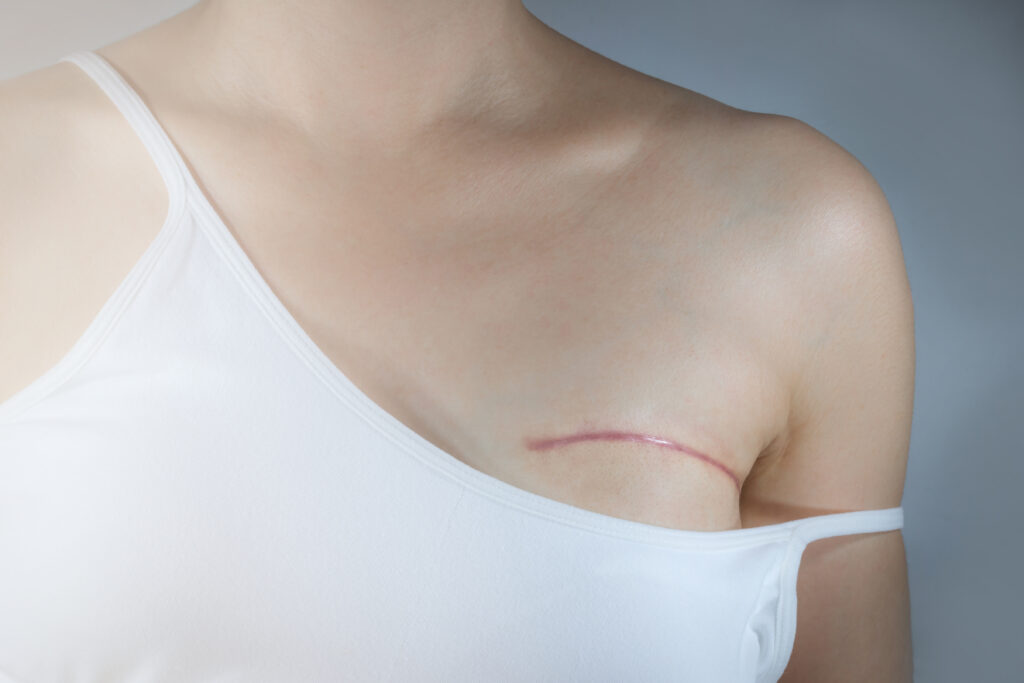
Breast reconstruction uses traditional plastic surgery techniques to make a new breast shape following an operation to remove the breast (mastectomy) to treat breast cancer or risk reduction surgery.
The aim is to recreate the original breast shape, but this isn’t always possible. There are several options to help get the appearance of a natural breast and help those surviving cancer to improve their mental wellbeing during this difficult experience.
Types Of Breast Reconstruction
There are a vast array of breast reconstruction options. Broadly speaking, the two categories are Implant Reconstruction (using breast implants) and Autologous Reconstruction (using the patient’s own tissue).
Implant reconstruction involves a similar approach to traditional breast implants, where silicone implants or tissue expanders are used to replicate natural breast tissue and create volume and shape. Surgeons will place the implant behind the chest muscle (submuscular placement) or in front of it (pre-pectoral placement).
Autologous tissue reconstruction (sometimes known as flap surgery) involves taking living tissue from other parts of the body and attaching it to the breast to create a natural breast in place of the one that was removed. The tissue is usually taken from the back, abdomen or thigh and can be attached in two ways.
Pedicled flap surgery involves cutting some of the blood vessels in the new tissue but keeping others, and then inserting the tissue into a new pocket within the breast and attaching some of the blood vessels to the chest.
Free flap reconstruction surgery is a more complicated procedure that involves disconnecting all of the blood vessels from the autologous tissue and then attaching it using new blood vessels.
When choosing the right option, the decision is always patient-centred, with some core factors including your natural breast shape, lifestyle and whether chemotherapy or radiotherapy are required after surgery.
Every patient will be given full information to ensure that they make an informed choice. Breast reconstruction surgery with Andrew Pieri involves a supportive and experienced team to ensure they get the support they need.
When To Have Breast Reconstruction
Increasingly, breast reconstruction is performed during the same operation as the mastectomy (termed immediate reconstruction) as opposed to delayed reconstruction, which is performed months or years later. There is evidence to show that this increases patient satisfaction with the reconstruction and reduces psychological morbidity in the long term.
The main practical advantage of immediate reconstruction is that the native breast skin (and often the nipple) can be preserved during the operation, and thus, only the breast volume needs to be replaced to achieve reconstruction. Assuming that the patient is fit for a reconstruction procedure, the decision is largely down to the individual’s choice and remains funded by the NHS in breast cancer (or risk reduction) surgery cases.
Full breast reconstruction often requires multiple procedures, and as such, getting immediate reconstruction following breast cancer surgery can be a quicker way towards the patient’s final goal of natural-looking breasts.
Preparing For Breast Reconstruction Surgery
Before breast reconstruction surgery, patients need to consider their lifestyle. Some factors, such as smoking or being overweight, can affect the outcome of the procedure.
As such, patients who are looking to get breast reconstruction following breast cancer treatment should aim to maintain a healthy weight and stop smoking or vaping before the procedure. These simple changes will help to improve the potential outcome.
Some existing health conditions, such as severe lung or cardiovascular diseases, can cause complications for breast reconstruction surgery, and in this case, treatment for these issues might be required before the reconstruction surgery can go ahead.

frequently asked questions
Which Is The Best Type Of Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
Each type of breast reconstruction surgery is different, and the best option for each patient depends on a number of factors, including their preference, lifestyle and ongoing breast cancer treatment needs. The breast reconstruction surgeon will discuss all the types of breast reconstruction surgery and guide patients towards the best choice.
How Long Does It Take To Heal From Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
Most women start to regain full body function and return to normal activities around 6-8 weeks after breast reconstruction surgery. If free flap autologous breast reconstruction surgery is performed, this may take longer to heal.
Is Breast Reconstruction Surgery Painful?
Every patient’s pain threshold is different, but most report moderate pain for 2-3 days post-breast reconstruction surgery. Sensations can come and go throughout the recovery period, but the issues usually subside after a few months.